
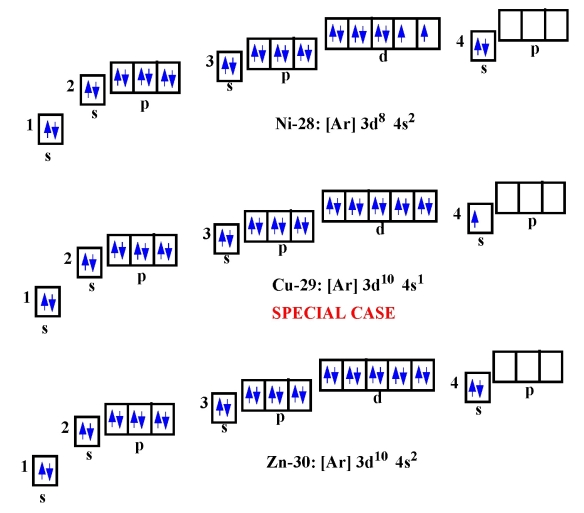
If the valence shell of an element is full, such as with a noble gas, then the element does not want to gain or lose an electron.įor example, alkali metals, which all have a valency of 1, want to lose that one electron and are likely to form ionic bonds (such as in the case of NaCl, or table salt) with a Group 17 element, which has a valency of 7 and wants to gain that one electron from the alkali metal (Group 1 element) to form a stable valency of 8.įor more on valence electrons and how they're related to the periodic table, I strongly recommend this video:Ĭitations: Tyler Dewitt. The valence is a numerical characteristic of the ability of atoms of a given element to bond with other atoms. The valence electrons for neon (Ne) are therefore eight. The electron configuration of neon indicates that the last shell has eight electrons (2s2 2p6). Valence electrons of Krypton The number of valence electrons in a Krypton atom - 8. They determine how "willing" the elements are to bond with each other to form new compounds. A valence electron is the total number of electrons found in a valenceshell. Valence electrons are responsible for the reactivity of an element. You can easily determine the number of valence electrons an atom can have by looking at its Group in the periodic table.įor example, atoms in Groups 1 and 2 have 1 and 2 valence electrons, respectively.Ītoms in Groups 13 and 18 have 3 and 8 valence electrons, respectively.
Valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost shell of an atom. To form a covalent bond, one electron from the halogen and one electron from another atom form a shared pair.įor example, in #"H–F"#, the dash represents a shared pair of valence electrons, one from #"H"# and one from #"F"#. To form an ionic bond, a halogen atom can remove an electron from another atom in order to form an anion (e.g., #"F"^"-", "Cl"^"-"#, etc.). Krypton has atomic number 36 and electron configuration1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p6or simply,Ar 3d10 4s2 4p6The electron configuration of krypton is: Ar3d10 4s2 4p6. They have one less electron configuration than a noble gas, so they require only one additional valence electron gain an octet. Hydrogen has its only electron in the 1s orbital - 1s1, and at helium the. The most reactive nonmetals are the halogens, e.g., #"F"# and #"Cl"#. UK syllabuses for 16 - 18 year olds tend to stop at krypton when it comes to. Nonmetals tend to attract additional valence electrons to form either ionic or covalent bonds. They need to lose only one or two valence electrons to form positive ions with a noble gas configuration. The most reactive metals are those from Groups 1 and 2. Generally, elements in Groups 1, 2, and 13 to 17 tend to react to form a closed shell with a noble gas electron configuration ending in #ns^2 np^6#. Elements whose atoms have the same number of valence electrons are grouped together in the Periodic Table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
